Sudoku Strategies: Y-Wings (or XY-Wings)
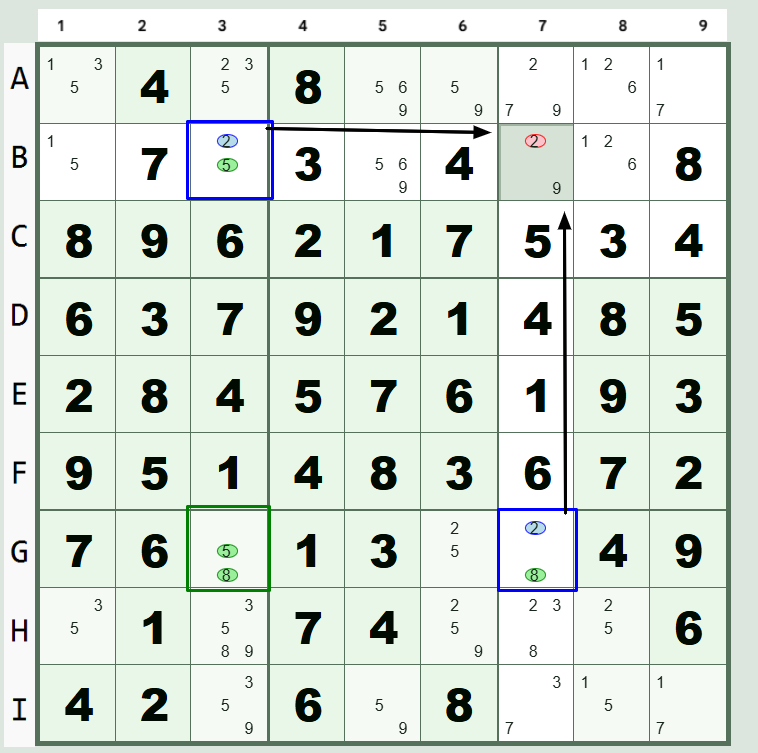
The Y-Wing (XY-Wing) Sudoku Technique
The "Y-Wing", also known as the "XY-Wing", is an advanced Sudoku solving strategy used to eliminate candidates in complex scenarios. It involves identifying a specific pattern of three bi-value cells (cells with exactly two candidates) that form a chain of relationships.
How the Y-Wing Works
The logic relies on a simple if-then chain. The three cells contain a total of three different candidates (let's call them X, Y, and Z) in specific combinations: (X, Y), (X, Z), and (Y, Z).
Key Components
- Pivot Cell (Cell "G3" in the illustration): The cell that "sees" (shares a row, column, or 3x3 box with) both of the other two cells. It has candidates X and Y. In this illustration, candidates "5" and "8").
- Pincer Cells (Cells "B3" and "G7" in the illustration): The two other cells, each with candidates X and Y (cell "B3" with candidates "2" and "5") and Y and Z (cell "G7" with candidates "2" and "8"). They must each see the pivot cell but do not necessarily have to see each other.
- Common Candidate: The candidate (Z, or "2" in this case) that appears in both pincer cells.
The Logic
Consider the pivot cell "G3". It must be either 5 or 8:
- If the pivot is "5", then "B3" must be "2".
- If the pivot is "8", then "G7" must be "2".
In both possible scenarios, one of the pincer cells is guaranteed to be "2". Therefore, any other cell in the Sudoku grid that "sees" *both* pincer cells simultaneously cannot contain the candidate "2", allowing for its elimination. In this case the elimination is of candidate "2" in cell "B7".
Step-by-Step Guide to Spotting a Y-Wing
Follow these steps to find and apply the technique:
- Pencil in all candidates: Ensure your grid is fully marked with all potential candidate numbers in each cell.
- Locate bi-value cells: Look for cells with exactly two candidates remaining. The Y-Wing uses three such cells.
- Identify a potential pivot: Find a bi-value cell (X, Y) that shares at least one house (row, column, or box) with two other bi-value cells (pincers).
- Confirm the pincer candidates: Verify that the pincers have the candidate combinations (X, Z) and (Y, Z), where Z is the common elimination candidate.
- Find the intersection: Locate any third cell(s) that "sees" *both* pincer cells (is in the same row/column/box as both).
- Eliminate the common candidate (Z): The candidate Z can be safely eliminated from any cell(s) found in step 5.

